Using quant_purger
The optional quant_purger submodule adds cache tag support for Quant content seeding. This relies on the Purge API and allows the Quant module suite to identify pages (including related content) that require updating based on user actions and then queues them for seeding.
How does it work?
Section titled “How does it work?”The quant_purger module creates a reference database table (purge_queuer_quant) that is used to map Drupal-generated cache tags to paths that have been seeded to Quant.
When Drupal issues a cache clear event, the Purge module collects that information and exposes it so that reverse proxies can be invalidated. In Quant’s use case, this provides an entry point for the Quant module suite to identify which cache tags require clearing and use that information to create queue entries that can be seeded to Quant on the next queue run.
The queued content will be processed during the next core cron run. You can run the cron manually or wait for the site’s cron to run on its regular schedule. For the latter, note that the static content will be out-of-sync with the Drupal site until the cron runs, which may cause confusion in some cases. Thus, it is recommended that cron is run right after content is edited if there are key pages that show the updated content.
- Enable the
quant_purgermodule - Seed your content to create entries in the reference database table
Additional configuration
Section titled “Additional configuration”Path and tag lists
Section titled “Path and tag lists”Drupal has a large number of cache tags, so some common cache tags are in the tag blocklist by default as they appear on every page (e.g., rendered). You can remove any of the default tags but keep in mind this may have a negative performance impact.
In order for cache tag purging to be effective and efficient, inspect the cache tags that are present for the URLs in the reference database table and update the tag blocklist with tags to exclude. For example, if you don’t want content to be queued for seeding when a particular media item is updated, you can add the cache tag for that media item to the tag blocklist.
- Enable the
purge_uicompanion module - Navigate to
/admin/config/development/performance/purge - Edit the Purge Quant queuer configuration
- Update the tag blocklist as needed
You can also update the path blocklist if there are certain paths that you don’t want to be queued for seeding during cache clear events.
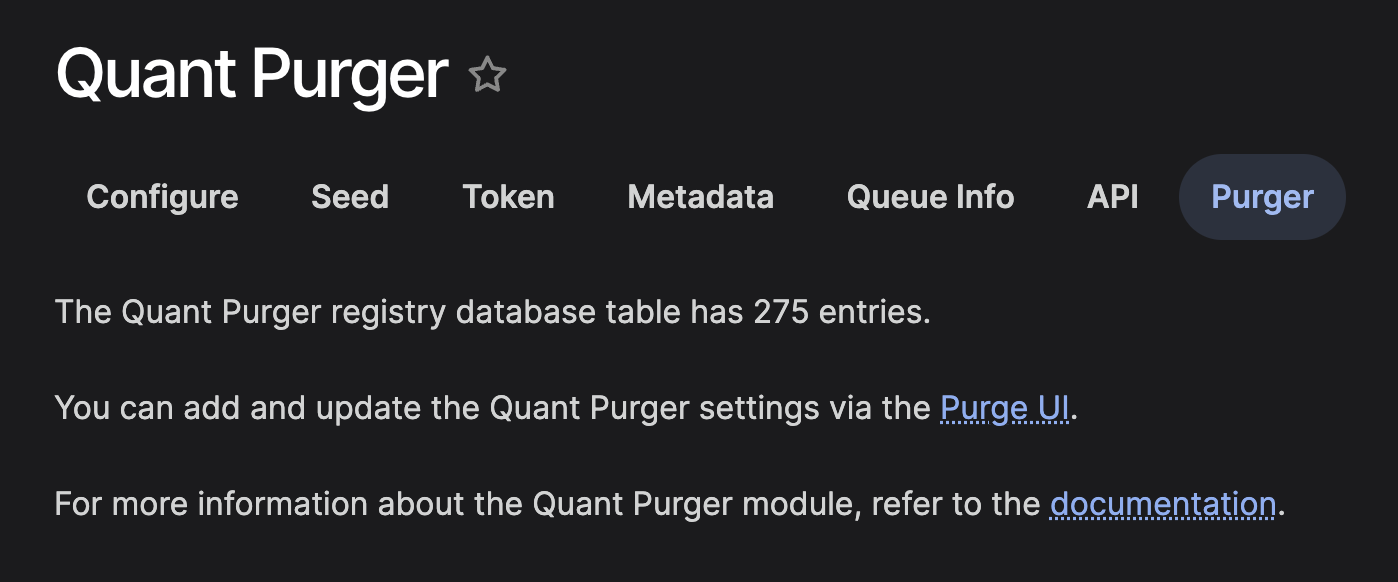 The Quant Purger tab in the Drupal UI links to the Purge UI.
The Quant Purger tab in the Drupal UI links to the Purge UI.
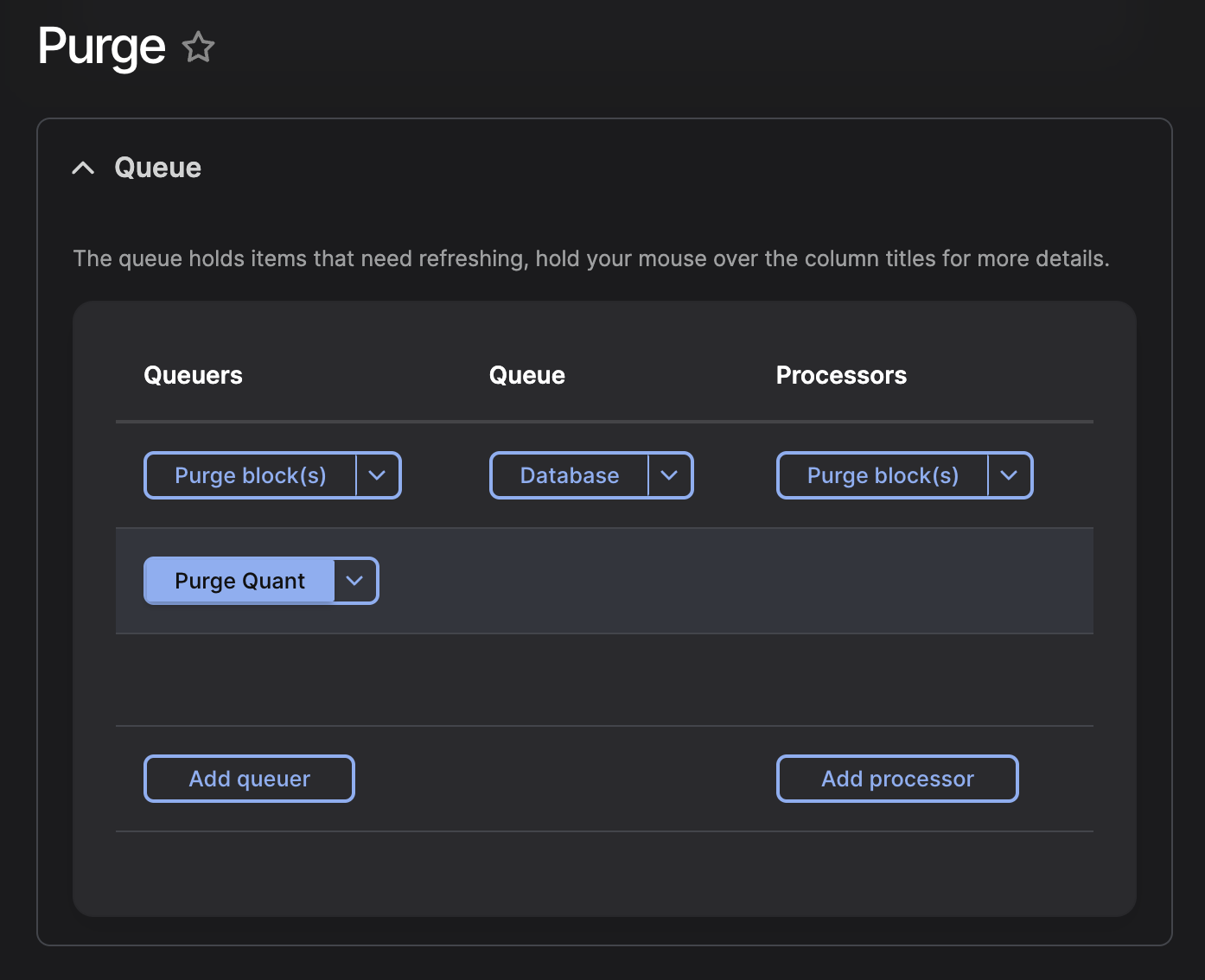 The Purge UI allow you to update the Quant Purger configuration.
The Purge UI allow you to update the Quant Purger configuration.
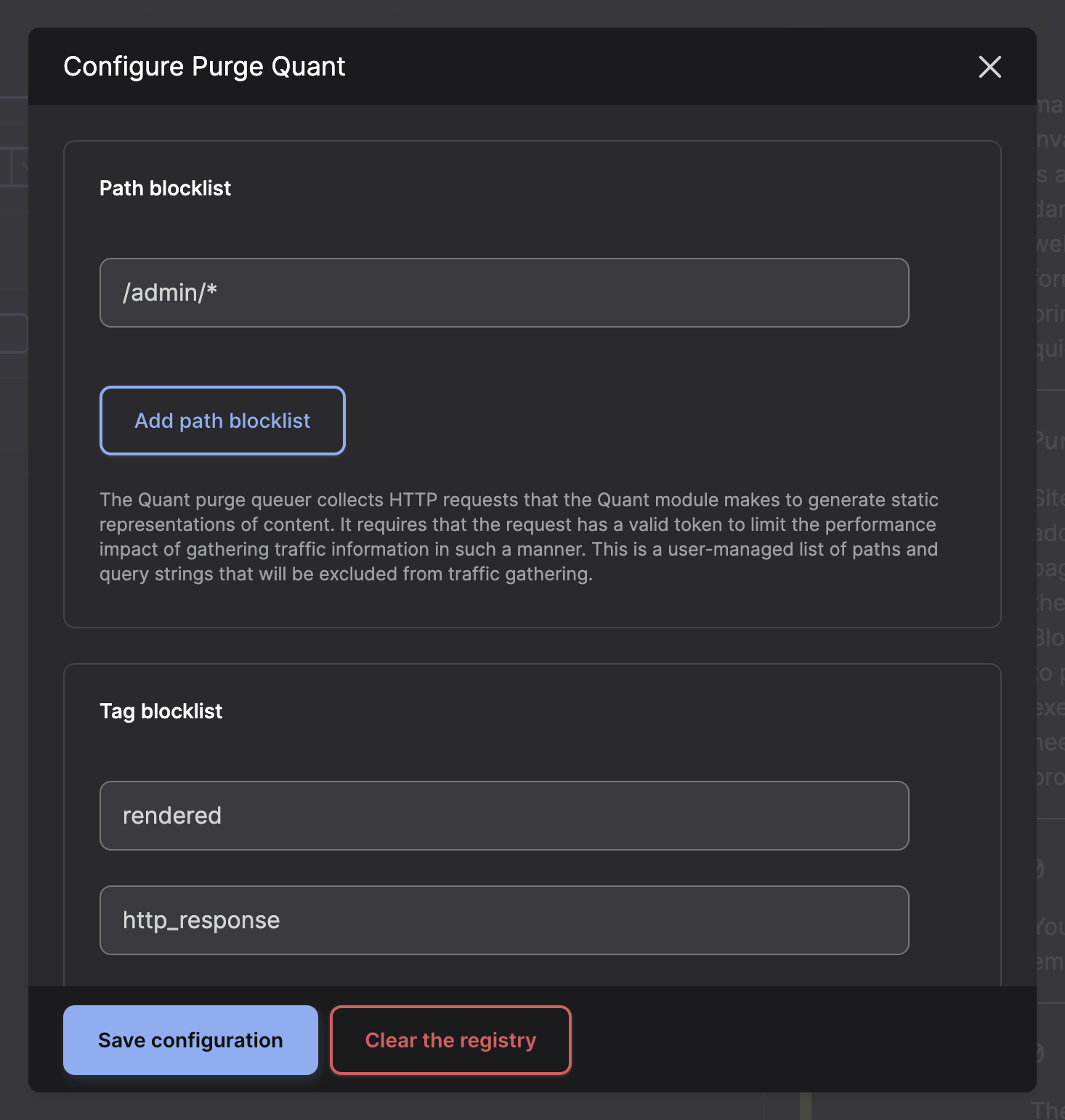 The path and tag blocklists can be modified in the Quant Purger configuration.
The path and tag blocklists can be modified in the Quant Purger configuration.
If you want to delete the values from the reference database table, you can use the Clear the registry button through the Purge UI or you can delete them directly in the database. In order to populate the table again, you must run a seed.
drush sqlq "delete from purge_queuer_quant"Performance tuning
Section titled “Performance tuning”For the best performance, it is highly recommended that your settings.php file includes:
$settings['queue_service_quant_seed_worker'] = 'quant.queue_factory';This changes the database driver that is used when managing the purge queue. Drupal’s database queue driver creates a unique item each which leads to duplicate items being added to the queue which will negatively impact the seed time for your website. The driver provided by Quant is optimised for Quant’s used case.
Example usage
Section titled “Example usage”A site has blog posts with category taxonomy terms shown on them. The names of the categories change sometimes, but the editorial team has decided that it’s not critical for these changes to be reflected on the static website quickly.
There is already a process in place for reseeding the site during each weekly development release. The editors have agreed that it’s okay if the category changes don’t show up until the weekly reseeding happens. So, the developers add the cache tags for these taxonomy terms to the tag blocklist.
When an editor changes one of these category terms, none of the associated content is queued for reseeding, which is what they want. Later, they decide to reverse this policy and remove the cache tag from the tag blocklist. Now, when an editor changes a category term, all the content associated with that term is queued for seeding.
They are using the quant_cron module to process a certain number of items from the queue during each cron, so it handles these new queue items. Occassionally, they run the seed processing with drush quant:run-queue when they want to make sure all the pressing changes show up.
